Stem cell therapy
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are precursor cells that are able to transform themselves into different types of tissue (bone, tendon tissue, cartilage tissue). They play a role in natural regeneration.
Stem cells are able to support and improve the body’s own regeneration when used therapeutically. It is currently not possible to regenerate entire tendons or entire joints using stem cells.
Indication
- Conservative therapy of arthrosis (degenerative joint disease with cartilage damage)
- Injuries and disorders to muscles and tendons
- as a supplementary therapy for operations on tendons and ligaments
- to improve bone healing
How are stem cells obtained?
In clinical use, stem cells are obtained from:
- bones on the iliac crest
- from adipose tissue of the abdomen
Stem cells are obtained from the iliac crest by means of local anesthesia and subsequent puncture of the bone with a needle. Stem cells are obtained from adipose tissue by making a small incision on the abdomen and then sucking off fat, as is done with liposuction during aesthetic surgery.
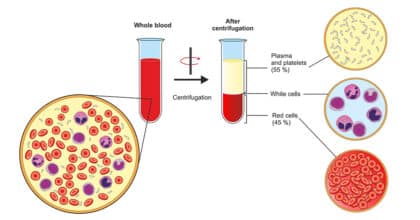
In both cases, the stem cells obtained are purified by centrifugation steps and concentrated for application. Depending on the indication, the cells are then applied to the joint, tendon or bone using a syringe.
What are the risks?
There may be bruises or discomfort at the removal site on the abdomen or iliac crest.
As with all interventions, there is a low risk of inflammation and infection at the application site.
