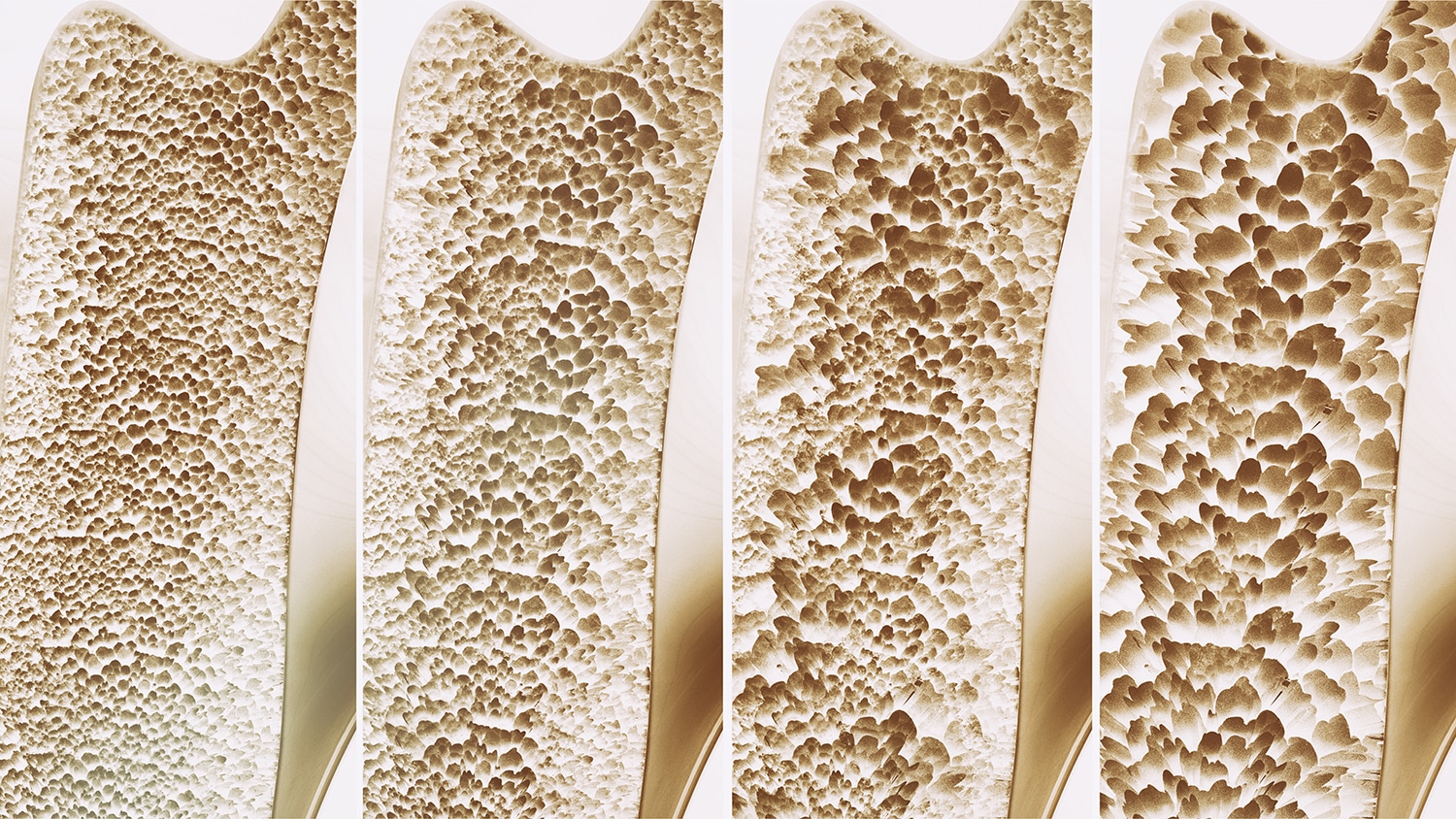
Osteoporosis
Prevention is better than cure. What is well known in general public has increasingly moved into the focus of health policy in recent years. Prevention should prevent the development of diseases as much as possible, or identify them at an early stage in order to stop or slow down the process.
Osteoporosis is a widespread disease that causes bone loss, especially with increasing age. As a result, bone fractures can occur even with small loads, which are associated with pain and costly treatment. A distinction is made between different types of osteoporosis (primary, secondary). Early detection and treatment can slow down or stop the progression and prevent the formation of fractures. Osteoporosis prevention is recommended for:
Women from the age of 50 | Men from the age of 55
The preliminary examination contains:
- Clinical examination
- Bone density measurement
- Blood test
- Urine test
- Diagnostics
- Risk assessment
- Therapy recommendation